BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
Breast Reconstruction in Fairfield County
Dr. Laurel Chandler performs breast reconstruction in Fairfield County at both Norwalk Hospital and St. Vincent's Medical Center. She performs breast reconstruction both in a delayed fashion or in conjunction with a breast surgeon at the time of mastectomy. At your first consultation, a full discussion will be held to discuss all factors that go into planning your surgery, in order to inform you so that the best decisions can be made regarding your care.
Dr. Chandler is the author and creator of the website, breastimplantinquiry.com, an educational website to inform patients about breast reconstruction and breast implants. In addition, she is first author of "Delay techniques for nipple-sparing mastectomy: A systematic review" published in the Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery in 2017 and has lectured on the topic nationally.
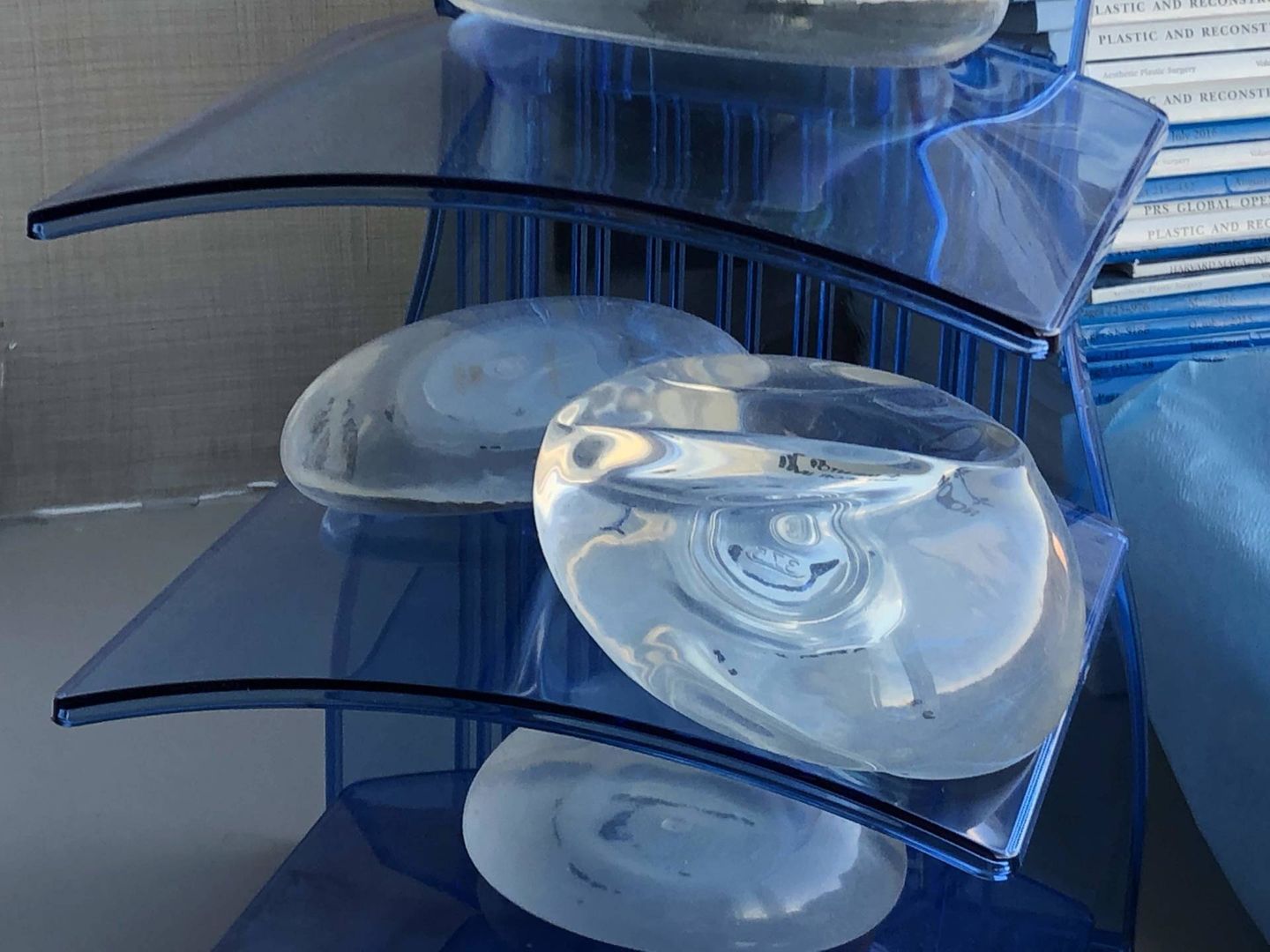
Implant-based breast reconstruction may begin with placement of a tissue expander with or without ADM (acellular dermal matrix) at the time of your mastectomy, and followed by exchange of the tissue expander for a permanent implant a few months later (as a second surgery). Alternatively, sometimes the permanent implant can be placed at the time of mastectomy (called “direct-to-implant reconstruction”) if you have small breasts, are not planned for any radiation treatment and have a healthy skin envelope after the mastectomy. The skin envelope must be enough to hold the implant at the time of mastectomy. If there is not enough skin, or you want larger breasts or have radiation planned, a tissue expander is a better first option because it allows expansion of the skin around the expander after the mastectomy. Expansion is usually completed in the office setting before radiation begins, because this limits the risks of wound healing and infectious complications caused by radiation. Downsides to implant-based reconstruction include accepting the risks of breast implants.
Autologous reconstruction involves reconstructing the breast using your own tissue, usually from the belly or the back. This is the best option if you have a history of breast radiation or want to avoid breast implants. There are different types of autologous reconstruction. Tissue may be taken from the abdomen, back, buttock or inner thigh to reconstruct the breast. Sometimes autologous tissue is used in conjunction with an implant in order to provide adequate volume and healthy tissue over the implant.
Subpectoral vs. Prepectoral Tissue Expander Placement
There are two types of tissue expander or implant placement in your body - below or above the pectoralis major muscle. Traditionally, expanders and implants are usually placed below the muscle because the muscle provides a layer of healthy, vascularized tissue that both camouflages the expander or implant and protects it from exposure and wound breakdown. In some cases, you may be a candidate for above-the-muscle placement if you have very healthy skin flaps at the time of mastectomy. This is not usually known until the time of the mastectomy. The benefit to this approach is mainly that you may experience less pain in recovery. Downsides to this approach include the implant may be more visible or palpable, and there may be a step-off deformity in the upper pole without the muscle to smooth out the breast contour.
Mastectomy Incisions
There are many different types of mastectomy incisions, and the incision type depends on whether or not the nipple is able to be preserved. If the nipple is not preserved, a traditional elliptical incision pattern is usually used, resulting in a horizontal linear scar across the center of the breast. This is a safe incision that provides good access for the breast surgeon to remove breast tissue sufficiently. Another option is a wise-pattern incision, if there is a significant amount of extra skin present with a ptotic nipple. This is usually performed using a specialized technique called a de-epithelialized flap in order to preserve healthy tissue underneath the incision pattern. The reason this option is sometimes chosen over the traditional horizontal incision is to create a more appropriate breast shape and contour by removing the excess skin in two dimensions rather than a single dimension.
Nipple-sparing mastectomy incision options:
Particular attention is paid in planning the location of incisions for nipple-sparing mastectomy because of concerns over preserving blood supply to the nipple and areola. Many sources of blood flow to the nipple and areola are divided during the mastectomy procedure, so it is important to preserve as much of the blood supply through the skin surrounding the areola as possible. Recommended incisions include:
- Radial or radiolateral - from the lateral aspect of the areola heading out laterally
- Vertical - from the inferior aspect of the areola heading down toward the breast fold
- Inframammary - along the inferior breast fold, traveling horizontally
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Q&A:
Am I a candidate for implant-based breast reconstruction?
You may be a good candidate for implant-based breast reconstruction if you have no history of radiation to the breast and have small to medium sized breasts. Radiation to the breasts BEFORE mastectomy and reconstruction can cause damage to the breast skin envelope, which increases risk of complications in implant-based breast reconstruction. However, you can still have implant-based breast reconstruction if the radiation is planned AFTER reconstruction.
Does radiation damage the skin?
Radiation directly damages DNA and produces free radicals that in tern damage proteins and cell membranes. This also causes blood flow to slow down and increase risk of blood clotting. In effect, radiation damage slows down wound healing, reduces strength of wound repair, increases infection rate and risk of wound breakdown.
When does tissue expansion begin after surgery?
After your tissue expander is placed, expansion usually begins two weeks later, assuming there are no wound healing complications.
Does tissue expansion hurt?
No, usually tissue expansion does not hurt because the skin overlying the tissue expander is numb for some time after the mastectomy. Tissue expansion is performed using sterile technique in the office setting.
How frequently does tissue expansion occur?
The first expansion usually happens at two weeks after surgery. Thereafter, expansion can happen on a weekly basis. (203) 423-3132 cc is usually added at each expansion. An exception to this would be if you have pain, tightness, or skin changes which may delay your expansion.New Paragraph
How do you know when tissue expansion is complete?
Tissue expansion will continue until the skin around the expander is over-expanded by 10-20%, because there is always some skin retraction when the permanent implant is placed. In other words, the permanent implant will always need to be slightly smaller than the size of the final tissue expander volume. You should check the volume of your breasts after each expansion and let your surgeon know when you have reached the volume that you prefer in a bra. After you reach this preferred volume, you should undergo one more expansion to allow for over-expansion. The expansion process usually takes about 2-3 months after your initial surgery.
When will the permanent implant be put in?
After tissue expansion is complete, your plastic surgeon will usually wait about one additional month before surgery to exchange the expander for the permanent implant. This allows time for your tissues to settle into their new volume.
Will the permanent implant feel different from the tissue expander?
Yes, the permanent implant will feel softer and lighter compared to the tissue expander. Tissue expanders have a harder shell and are filled with saline, which makes them feel firmer and heavier compared to permanent implants. In addition, the permanent implant will be slightly smaller than the final tissue expander volume.
Call Us Now for a Consultation!